Incoterms explained: The terms that you need to know in international trade
Incoterms are an introductory need for every foreign trader. They are used almost everywhere in daily work, such as RFQ, CIF, FOB, and CFR, do you exactly know what they mean?
Today, GBI collects and sorts out the explanations of international commercial terms in the entire transaction process: From inquiry to payment, covering names, meanings, full English names, and English abbreviations, so that you will not be confused about these concepts anymore. Now learn and check it:
(1) Ex-Work (EXW)
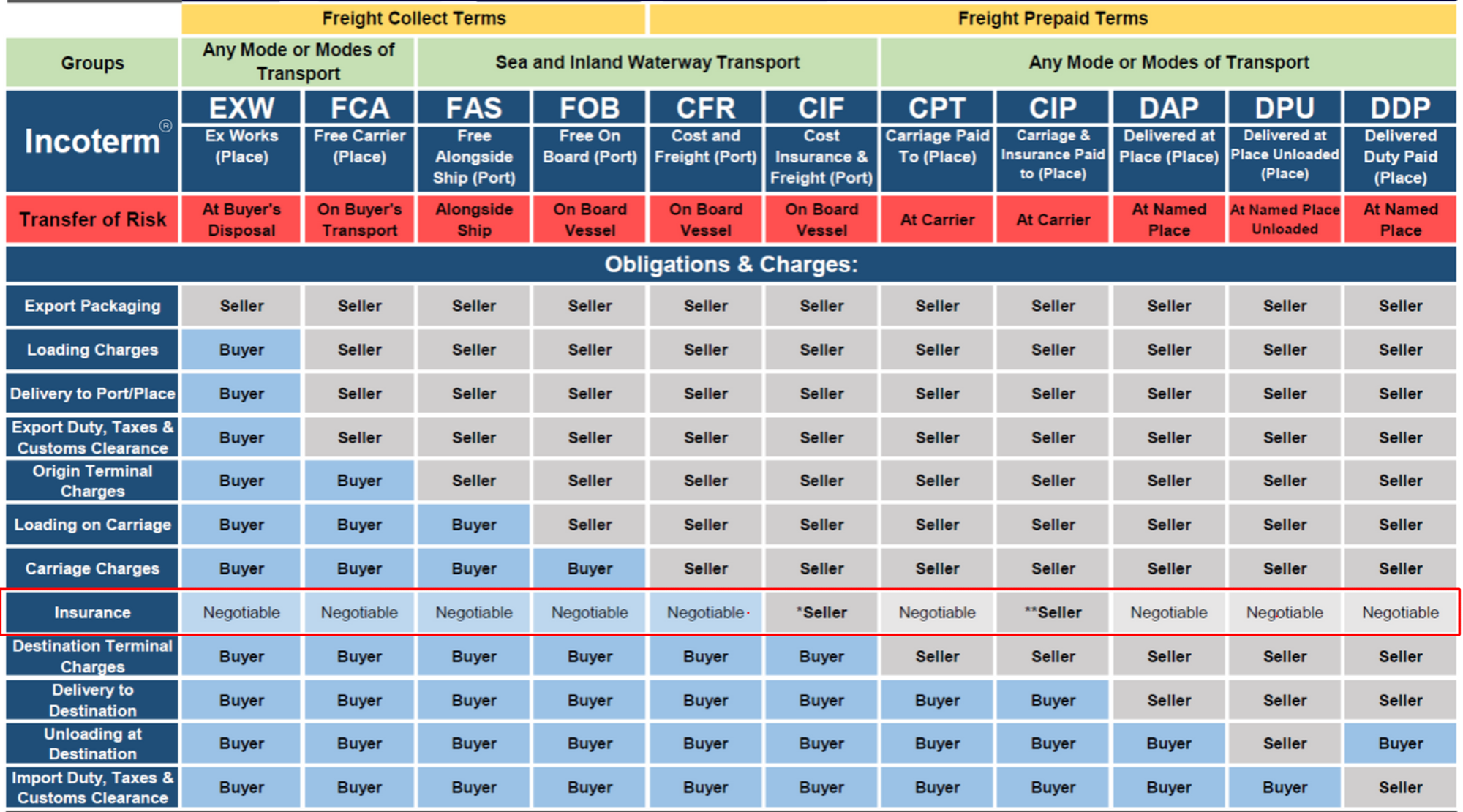
Ex-Work (EXW) means that the seller is responsible for delivering the prepared goods to the buyer at his place, namely the workshop, factory, warehouse, etc. But usually, the seller is not responsible for loading the goods on the vehicle prepared by the buyer, or clearing the goods. The buyer bears all costs and risks of transporting the goods from the seller’s place to the intended destination.

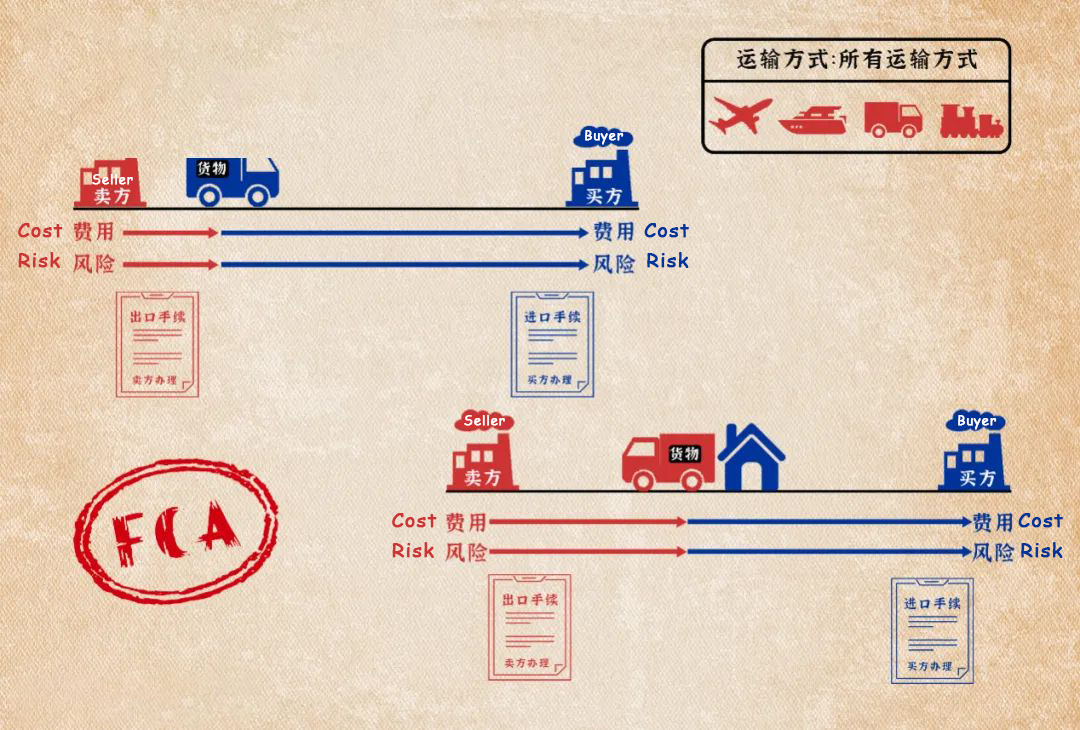
(2) Free Carrier (FCA)
Free Carrier (FCA) means that the seller is responsible for the delivery of the goods, and customs clearance. After these, the goods will be delivered to the carrier designated by the buyer in the care of the buyer. According to business practice, when the seller is required to cooperate with the carrier by signing a contract, the seller can adopt FCA if the buyer bears the risks and expenses. FCA can be applied to any mode of transportation.
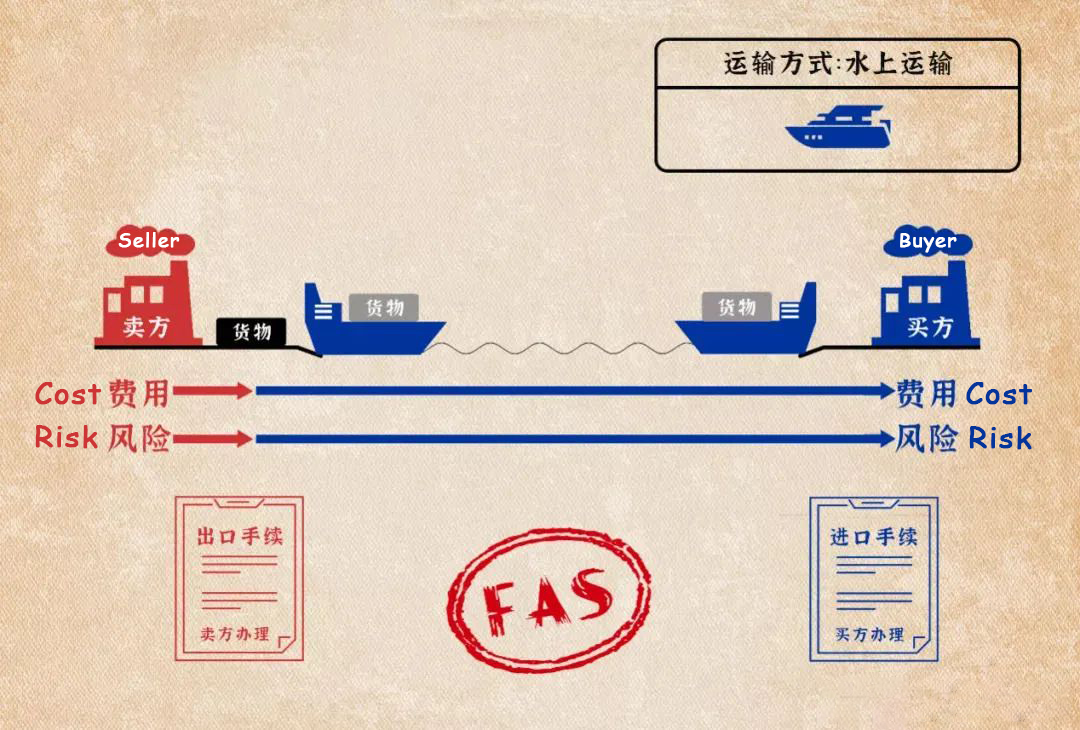
(3) Free Alongside Ship (FAS)
Free Alongside Ship (FAS) means that the seller delivers the goods to the side of the ship on the designated port of loading or barge. After this, the buyer needs to bear all the costs and risks of the loss and damage of the goods. The buyer also needs to go through export customs clearance procedures. FAS is suitable for sea or inland water transportation.
(4) Free on board (FOB)
Free on board (FOB) means that the seller delivers the goods after passing the ship’s rail at the designated port of shipment. After the goods passed the ship’s rail, the buyer shall bear all costs, risks, loss, or damage of the goods, and require the seller to go through customs clearance procedures for the export of the goods. FOB is suitable for sea or inland water transportation.
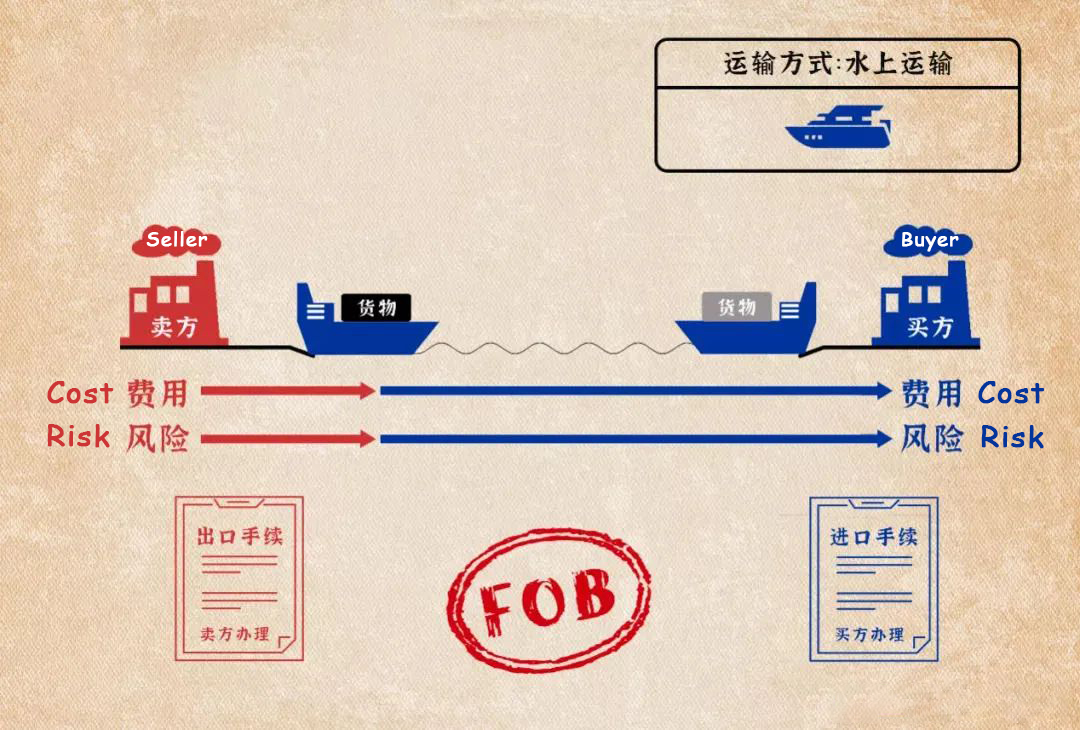
(5) Cost and Freight (CFR)
Cost and Freight (CFR) means that the seller needs to pay the expenses and freight required to transport the goods to the designated port of destination. However, after the goods are delivered to the ship’s deck, the risk of the goods, loss or damage, and the additional expenses incurred after an accident, the responsibility will turn to the buyer. In addition, the seller is required to go through customs clearance procedures for the export of the goods. CFR can be applied to sea or inland water.
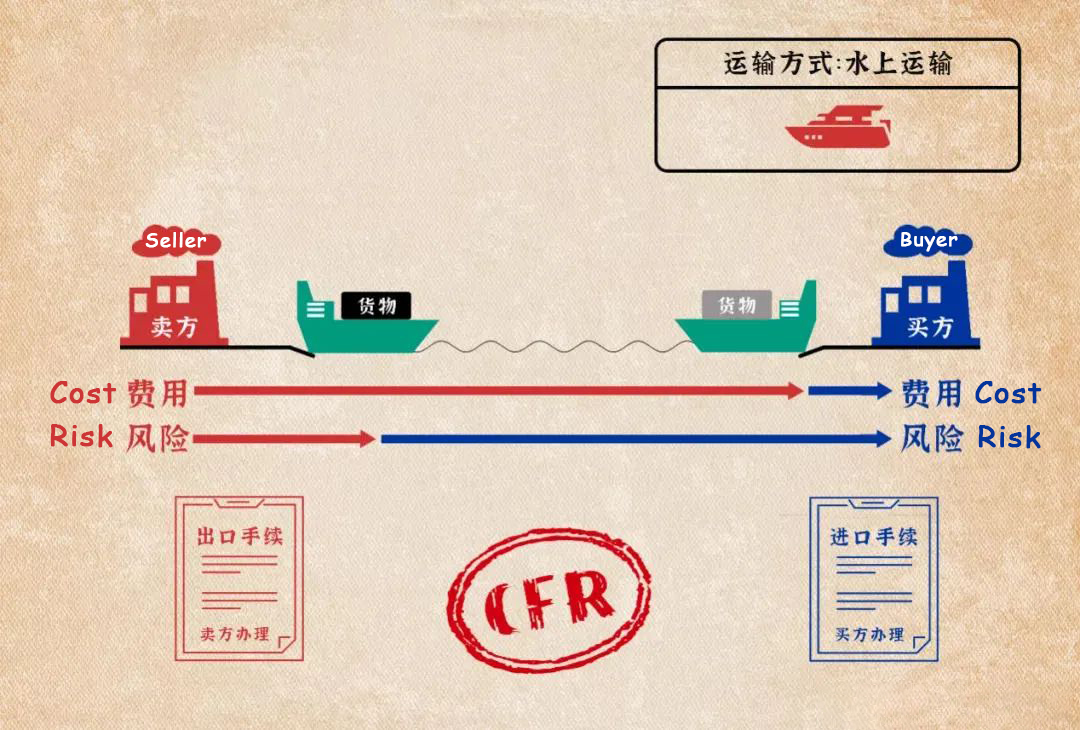
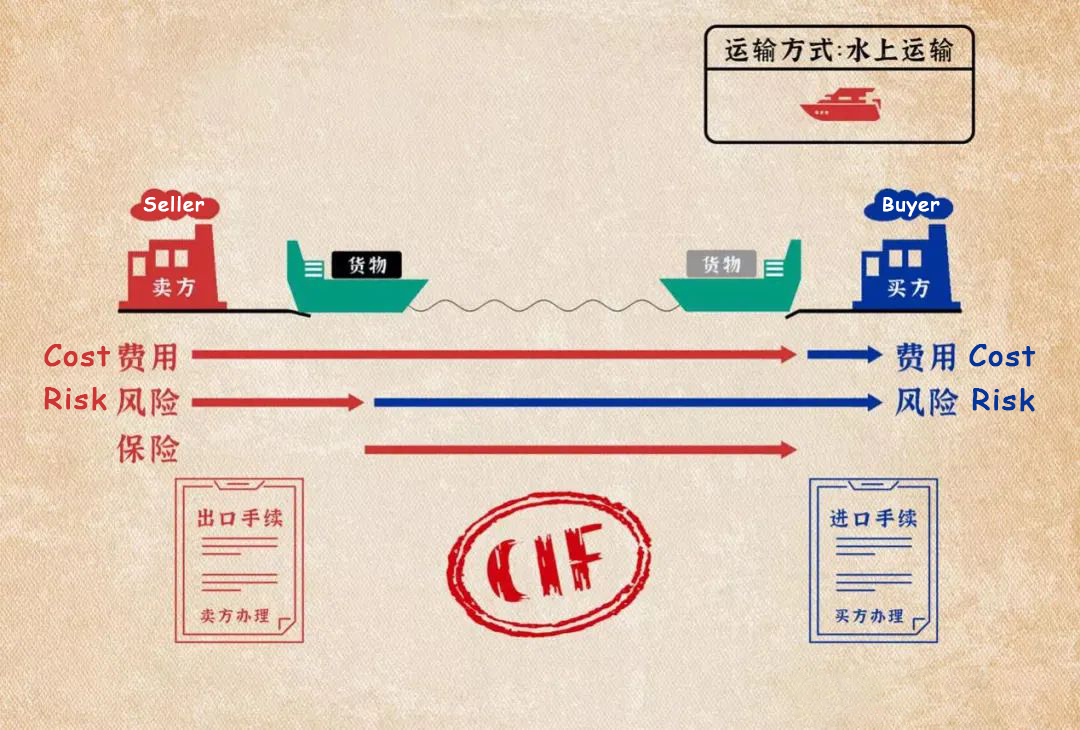
(6) CIF (Cost Insurance & Freight)
Cost Insurance & Freight (CIF) means that, in addition to the seller having the same obligations as CFR, the seller also needs to apply for marine insurance and pay the insurance premium for the loss or damage of the purchased goods while the goods are in transit. CIF is suitable for sea or inland water transportation.
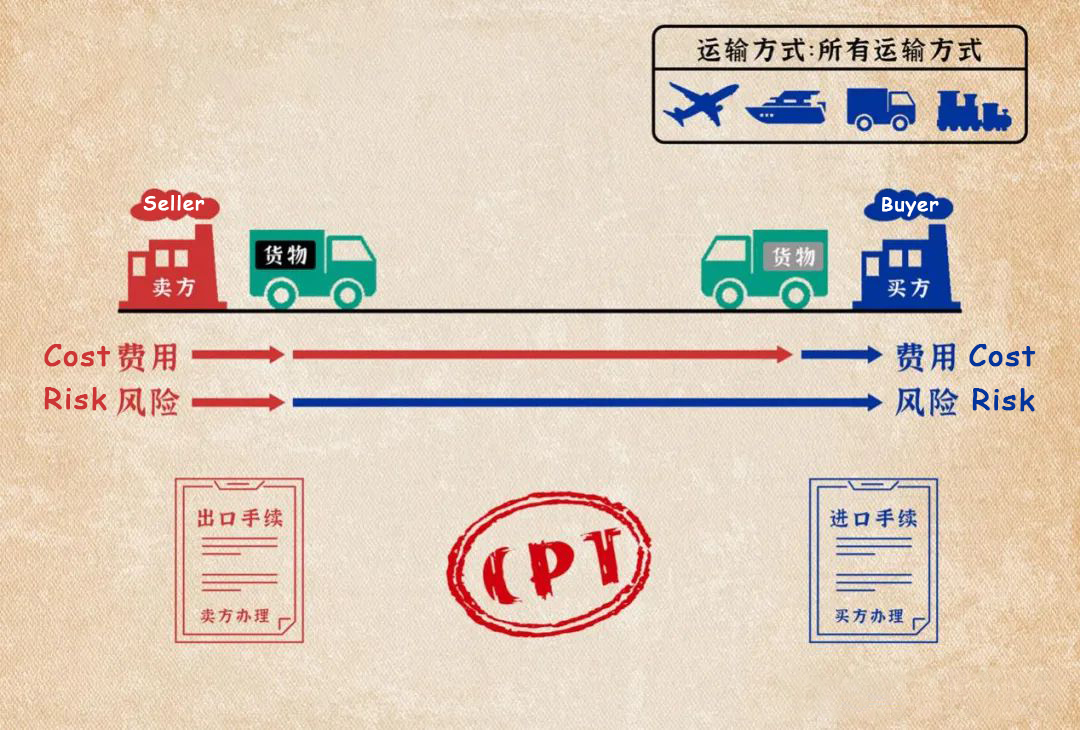
(7) Carriage Paid To (CPT)
Carriage Paid To (CPT) refers to the freight paid by the seller to transport the goods to the designated destination. The risk of loss or damage to the goods and any additional costs incurred in the event after the goods were delivered to the carrier shall be borne by the seller. In addition, the seller needs to go through customs clearance procedures for the export of goods. CPT is applicable to various modes of transportation, including multimodal transportation.
(8) Carriage & Insurance Paid To (CIP)
Carriage & Insurance Paid To (CIP) means that in addition to the seller’s obligations as CPT, the seller also needs to apply for maritime insurance against the risk of loss or damage to the goods. The buyer should also pay the insurance premium. It is applicable to any mode of transportation.
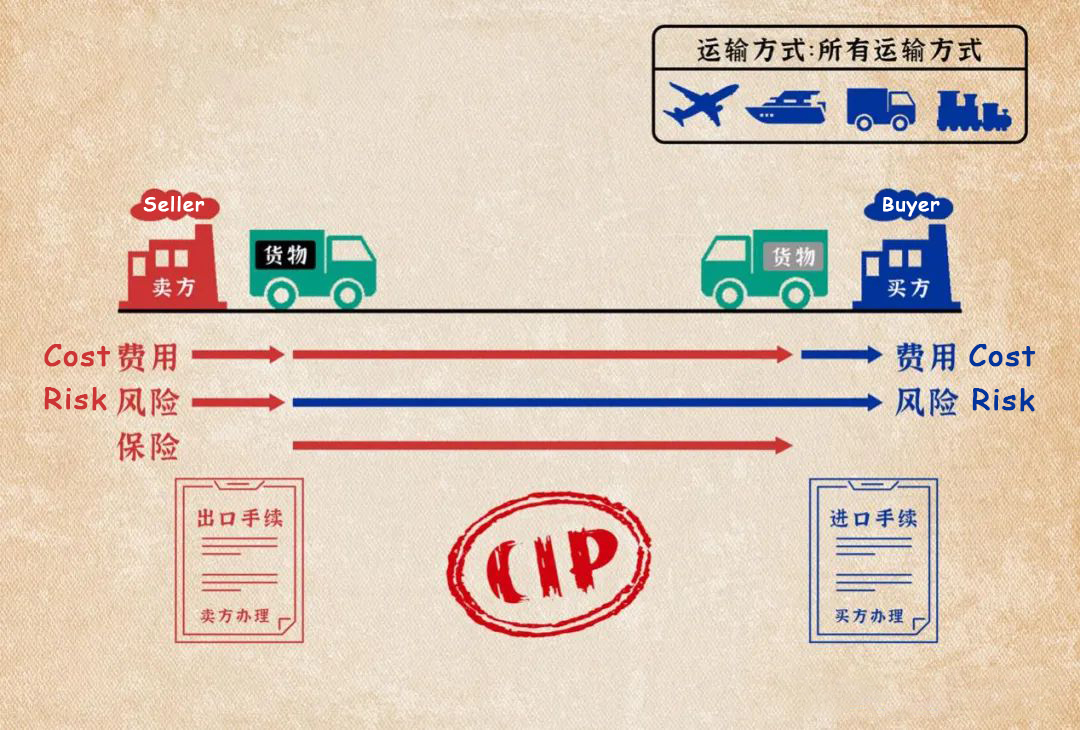
(9) Delivered At Place (DAP)
Delivered At Place (DAP) means that the seller is responsible for delivering the goods stipulated in the contract to the buyer within the prescribed time limit in accordance with the usual routes and customary methods. The goods are loaded and ready to be unloaded on the means of transport. All risks of shipping to the designated place. DAP is suitable for goods transported by rail or road, and can also be used for other modes of transportation.
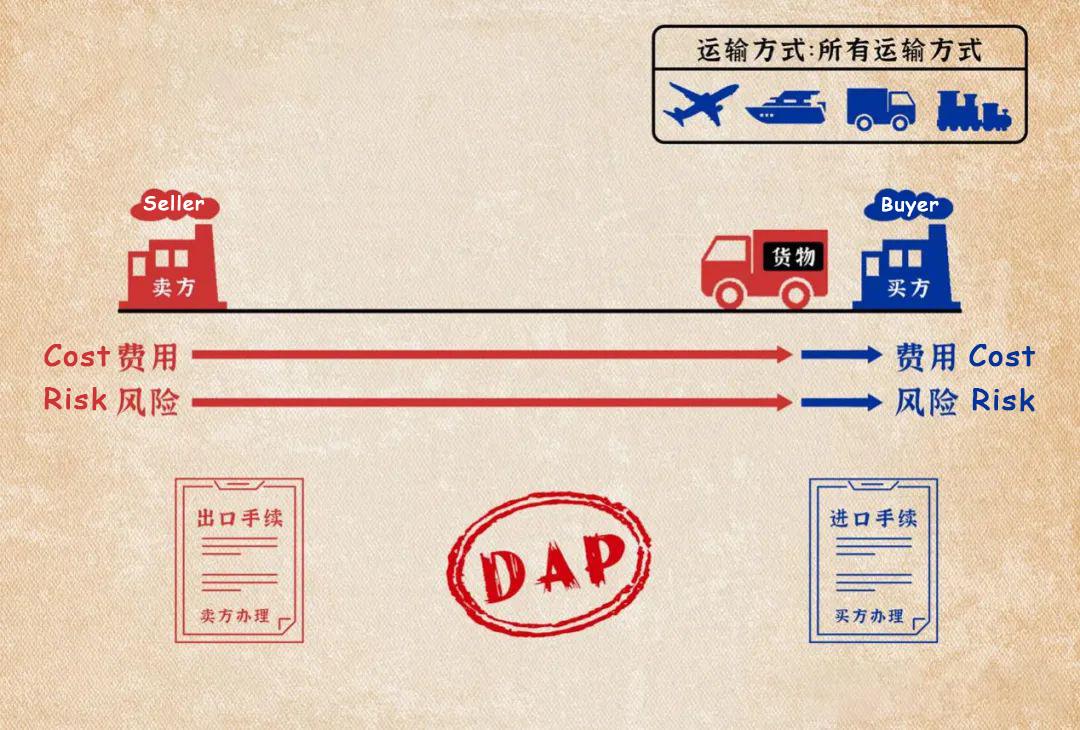
(10) Delivered at Place Unloaded (DPU)
Delivered at Place Unloaded (DPU) means that the seller needs to deliver the prepared goods at the place designated by the importing country, and bear all the costs and risks of the goods transported to the designated place (excluding customs duties, taxes, and other official duties that should be paid at the time of import). In addition to bear the costs and risks of customs procedures. The buyer should also bear the additional costs and risks caused by the failure to complete the customs clearance of the goods in time. DPU is suitable for various transportation methods.
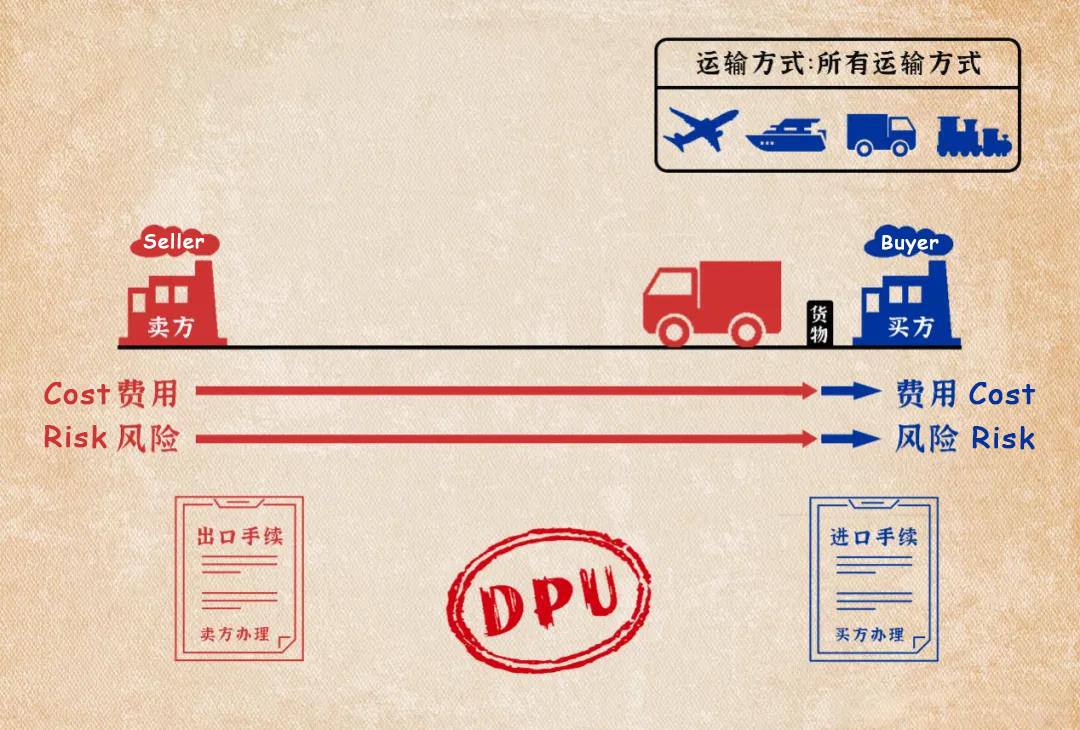
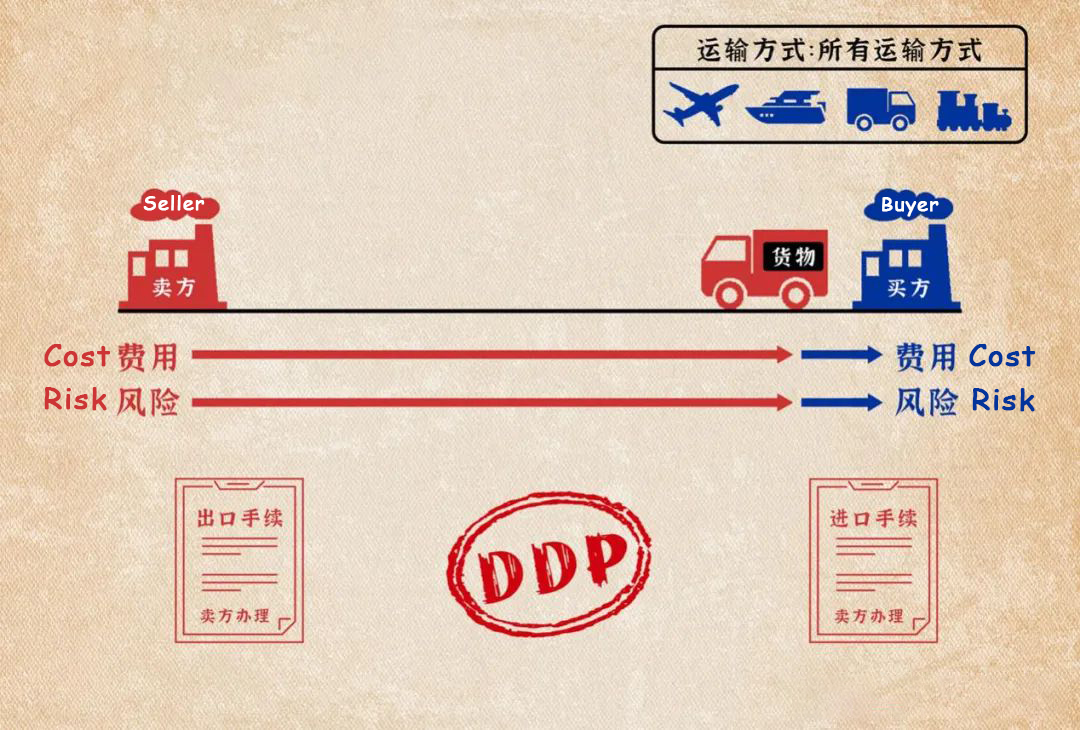
(11) Delivered Duty Paid (DDP)
Delivered Duty Paid (DDP) means that the seller needs to deliver the prepared goods at the designated place in the importing country, and bears all the costs and risks of transporting the goods to the designated place. It also needs to handles import customs clearance. DDP can be applied to various modes of transportation.